See also The BioPesticide Manual, 2nd Ed.
Plant growth regulator
gibberellins
NOMENCLATURE
Common name gibberellic acid (BSI, draft E-ISO, accepted in lieu of a common name); acide gibbérellique (draft F-ISO)
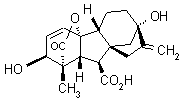
IUPAC name (3S,3aS,4S,4aS,7S,9aR,9bR,12S)-7,12-dihydroxy-3-methyl-6-methylene-2-oxoperhydro-4a,7-methano-9b,3-propeno[1,2-b]furan-4-carboxylic acid
Alt: (3S,3aR,4S,4aS,6S,8aR,8bR,11S)-6,11-dihydroxy-3-methyl-12-methylene-2-oxo-4a,6-ethano-3,8b-prop-1-enoperhydroindeno[1,2-b]furan-4-carboxylic acid
Chemical Abstracts name (1a,2b,4aa,4bb,10b)-2,4a,7-trihydroxy-1-methyl-8-methylenegibb-3-ene-1,10-dicarboxylic acid 1,4a-lactone
Other names gibberellin A3; GA3 (ambiguous) CAS RN [77-06-5]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 346.4 M.f. C19H22O6 Form Crystalline solid. M.p. 223-225 ºC (decomp.) Solubility In water 5 g/l (room temperature). Soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetone, and aqueous alkalis; slightly soluble in diethyl ether and ethyl acetate. Insoluble in chloroform. Potassium, sodium, and ammonium salts: Readily soluble in water (potassium salt 50 g/l). Stability Dry gibberellic acid is stable at room temperature, but slowly undergoes hydrolysis in aqueous or aqueous-alcoholic solutions, DT50 (20 ºC) c. 14 d (pH 3-4), 14 d (pH 7). In alkalis, undergoes a rearrangement to less biologically-active compounds. Decomposed by heat. pKa 4.0
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered by E. Kurosawa (Trans. Nat. Hist. Soc. (Formosa), 1926, 16, 213), who called it gibberellin A. Later ICI Plant Protection Ltd (now Syngenta AG) isolated a compound with similar biological properties and chemical structure, and this was called gibberellic acid. It and other members of the gibberellin group (over 70 are known) occur naturally in a wide variety of plant species. The establishment of its chemical structure and stereochemistry has been reviewed (J. F. Grove, Q. Rev. Chem. Soc., 1961, 15, 56; B. E. Cross et al., Adv. Chem. Series, 1961, No. 28, p. 13). Introduced by ICI (now Syngenta AG). Manufacturers Abbott; JIE; Jingma; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Acts as a plant growth regulator on account of its physiological and morphological effects in extremely low concentrations. Translocated. Generally affects only the plant parts above the soil surface. Uses Has a variety of applications, e.g. to improve fruit setting of clementines and pears (especially William pears); to loosen and elongate clusters and increase berry size in grapes; to control fruit maturity by delaying development of the yellow colour in lemons; to reduce rind stain and retard rind ageing in navel oranges; to counteract the effects of cherry yellows virus diseases in sour cherries; to produce uniform seedling growth in rice; to promote elongation of winter celery crop; to induce uniform bolting and increase seed production in lettuce for seed; to break dormancy and stimulate sprouting in seed potatoes; to extend the picking season by hastening maturity in artichokes; to increase the yield in forced rhubarb; to increase the malting quality of barley; to produce brighter-coloured, firmer fruit, and to increase the size of sweet cherries; to increase yields and aid harvesting of hops; to reduce internal browning and increase yields of Italian prunes; to increase fruit set and yields of tangelos and tangerines; to improve fruit setting in blueberries; to advance flowering and increase the yield of strawberries; and also a variety of applications on ornamentals. Application rates up to 80 g/a per application, depending on desired effect. Formulation types EC; SG; SP; TB; Crystals. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials and solutions containing chlorine. Selected tradenames: 'Activol' (Syngenta); 'Berelex' (Syngenta); 'Ceku-Gib' (Cequisa); 'GIB' (Burlington); 'Gibbex' (Griffin); 'Kri-Gibb' (Krishi Rasayan); 'ProGibb' (Valent Biosciences); 'Release' (Valent Biosciences); 'RyzUp' (Valent Biosciences); 'Strong' (Sanonda); mixtures: 'Fengib' (+ MCPA-thioethyl) (Hokko)
OTHER TRADENAMES
'Agro-Gibb' (AgroSan); 'Falgro' (Fine); 'Forgibbs' (Forward); 'GibGro' (Agtrol); 'Novagib' (Fine); 'Point Acigib' (Point Enterprise); 'Pol-Gibrescol' (Ciech); 'Ralex' (Valent Biosciences); 'Rasayanic Acid' (Krishi Rasayan); 'Ro-Gibb' (Rotam); 'Tigibb' (Tide); 'Vimogreen' (Vipesco) mixtures: 'Maxon' (+ 4-indol-3-ylbutyric acid) (Agro Distribution); 'PGR-IV' (+ 4-indol-3-ylbutyric acid) (Marman, Micro Flo) Discontinued names: 'Uvex' * (Productos OSA) mixtures: 'Zero-One' * (+ MCPA-thioethyl) (Hokko)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc; details available from Syngenta. Residues determined by tlc (V. W. Winkler, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 545).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >15 000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Non-irritating to skin and eyes. Inhalation No ill-effect on rats subjected to 400 mg/l for 2 h/d for 21 d. NOEL (90 d) for rats and dogs >1000 mg/kg diet (6 d/w). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (Table 5); EPA (formulation) III |